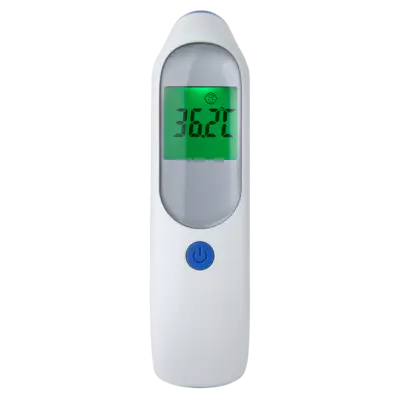
Forehead Thermometer
According to the difference of the purpose of use, a variety of thermometers have been designed and manufactured. Its design is based on: the use of the phenomenon of thermal expansion and contraction of solids, liquids, and gases under the influence of temperature; under the condition of constant volume, the pressure of gas (or vapor) changes due to the difference of temperature; the role of thermoelectric effect; The transformation of temperature; the influence of thermal radiation, etc.
1. Gas thermometer: use hydrogen or helium as the temperature measurement material, because the liquefaction temperature of hydrogen and helium is very low, close to absolute zero, so its temperature measurement range is very wide. This thermometer has high accuracy and is mostly used for precise measurements.
3. Thermocouple thermometer: It is a temperature measuring instrument widely used in industry. Made by thermoelectric phenomenon. Two different metal wires are welded together to form the working end, and the other ends are connected to the measuring instrument to form a circuit. When the working end is placed at the temperature to be measured, when the temperature of the working end and the free end are different, an electromotive force will appear, so a current flows through the loop. Through the measurement of electrical quantities, using the temperature at a known location, the temperature at another location can be determined. It is suitable for two substances with a large temperature difference, and is mostly used for high temperature and low turbidity measurement. Some thermocouples can measure high temperatures up to 3000°C, and some can measure low temperatures close to absolute zero.
4. Pointer thermometer: It is a thermometer shaped like a dashboard, also known as a cold and summer watch. It is used to measure the room temperature and is made of the principle of thermal expansion and contraction of metal. It uses a bimetallic sheet as a temperature sensing element to control the pointer. The bimetallic sheet is usually riveted with copper sheet and iron sheet, and the copper sheet is on the left and the iron sheet is on the right. Because the thermal expansion and contraction effect of copper is more obvious than that of iron, when the temperature rises, the copper sheet pulls the iron sheet to bend to the right, and the pointer is deflected to the right (pointing to high temperature) driven by the bimetallic sheet; otherwise , the temperature becomes lower, and the pointer is deflected to the left (pointing to low temperature) driven by the bimetallic sheet.
6. Pressure thermometer: The pressure thermometer uses the liquid, gas or saturated vapor in a closed container to generate volume expansion or pressure change as a measurement signal. Its basic structure is composed of three parts: temperature bulb, capillary tube and indicating table. The advantages of pressure thermometers are: simple structure, high mechanical strength, not afraid of vibration. Inexpensive and requires no external energy. The disadvantage is: the temperature measurement range is limited, generally -80~400℃; the heat loss is large and the response time is slow.
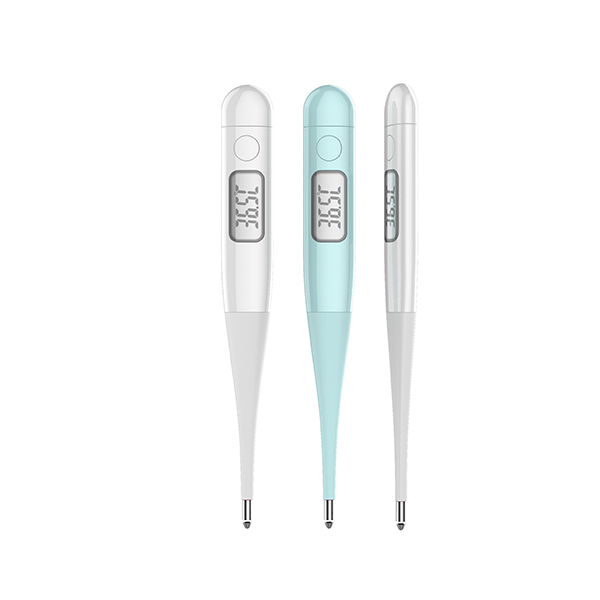
7. Mercury thermometer is a kind of expansion thermometer. The freezing point of mercury is -38.87°C and the boiling point is 356.7°C. It is used to measure the temperature within the range of 0--150°C or 500°C. It can only be used as an instrument for on-site supervision. Using it to measure temperature is not only simple and intuitive, but also avoids the errors of external remote thermometers.